
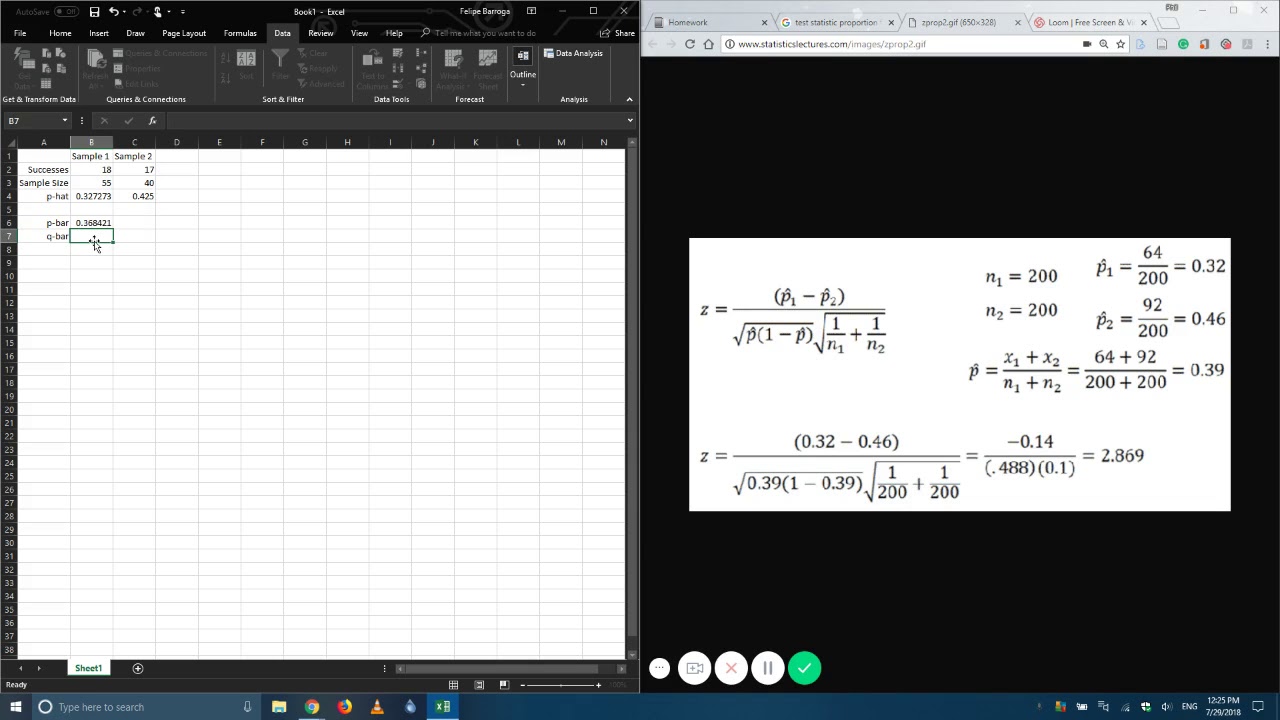
For Cp, Cpl, and Cpu, information about the process performance is supplied and for Cp a status information is given to facilitate the interpretation. A table contains the following indicators for the process capability and if possible the corresponding confidence intervals: Cp, Cpl, Cpu, Cpk, Pp, Ppl, Ppu, Ppk, Cpm, Cpm (Boyle), Cp 5.5, Cpk 5.5, Cpmk, and Cs (Wright). Process capabilities: These tables are displayed, if the "process capability" option has been selected.
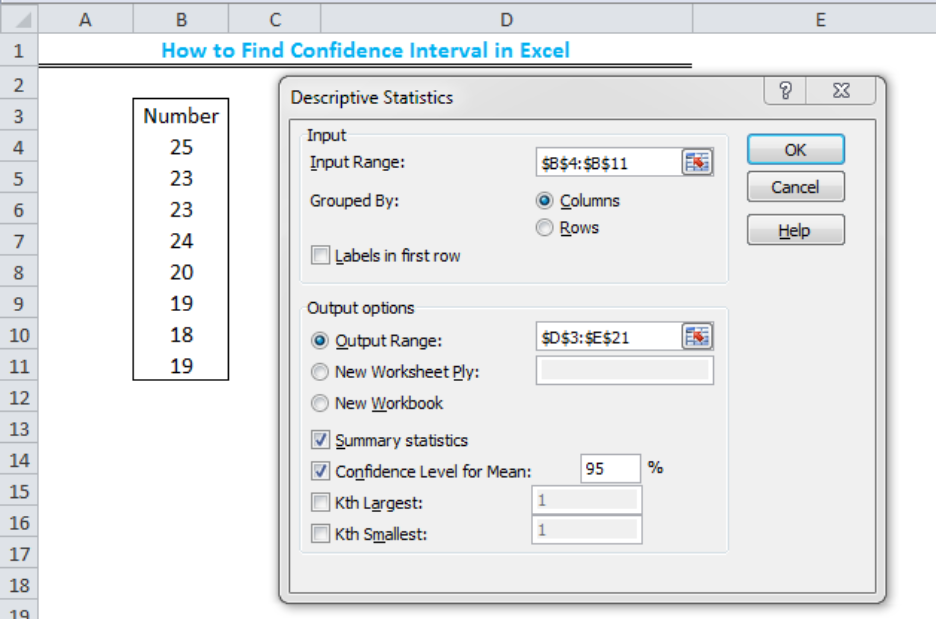
There will be one column for each phase.Process capabilities: This table contains information about the center line and the upper and lower control limits of the selected chart.
Xlstat calculate confidence interval series#
If it hasn’t then the transformed series is the direct application of the Box-Cox transformationX bar/ R/ S/ S² table If Lambda has been optimized, the transformed series corresponds to the residuals of the model. Series before and after transformation: This table displays the series before and after transformation. By the use of a normality test, you can verify these premises (see the Normality Tests in XLSTAT-Pro).Results for subgroup charts in XLSTATBox-Cox transformationĮstimates of the parameters of the model: This table is available only if the Lambda parameter has been optimized. Note: During the interpretation of the different indicators for the process capability please pay attention to the fact that some indicators suppose normality or at least symmetry of the distribution of the measured values. The S chart draws the standard deviation of the process and the S’² chart draws the variance (which is the square of the standard deviation). S and S’² charts are also used to analyze the variability of production.A large difference in production, caused for example by the use of different production lines, will be easily visible. An R chart (Range chart) is useful to analyze the variability of the production.Mean shifts are easily visible in the diagrams. An X bar chart is useful to follow the mean of a production process.The subgroup charts tool offers you the following chart types alone or in combination: Integrated in this tool, you will find Box-Cox transformations, calculation of process capability and the application of rules for special causes and Westgard rules (an alternative set of rules to identify special causes) to complete your analysis. This tool is useful to recap the mean and the variability of the measured production quality.Subgroup chart in XLSTAT The measurements need to be quantitative data. It is used to supervise production quality, in the case where you have a group of measurements for each point in time. Subgroup ChartsWhat is a subgroup control chartĪ subgroup chart is a type of control chart that focus on the quality characteristic measurement within one subgroup. All points are represented together with the median.XLSTAT 는 MS 엑셀에서 통계처리를 할 수 있도록 개발된 프로그램입니다. Scattergrams: These univariate representations give an idea of the distribution and possible plurality of the modes of a sample.In addition to the quantile plots, XLSTAT gives you the possibility to plot several charts: Confidence interval based on the normal distribution.You can obtain confidence intervals associated to the quantiles. Quantiles are useful because they are less sensitive to outliers and skewed distributions. While you can select several samples at the same time, XLSTAT calculates all the descriptive statistics for each sample independently. XLSTAT offers you five methods to calculate quantiles. The XLSTAT quantile tool calculates quantiles and displays univariate plots for a set of quantitative variables. There are q − 1 of the q-quantiles, one for each integer k satisfying 0 < k < q.Ī percentile is a quantile based on a 0 to 100 scale. The q-quantile of a variable X is given by: The kth q-quantile for a random variable X is the value x such that the probability that the random variable will be less than x is at most k / q and the probability that the random variable will be more than x is at most (q − k) / q.

Quantiles are defined by ordering data into q equally sized data subsets and noting the boundaries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
